ANATOMY OF PERIPHERAL NERVES
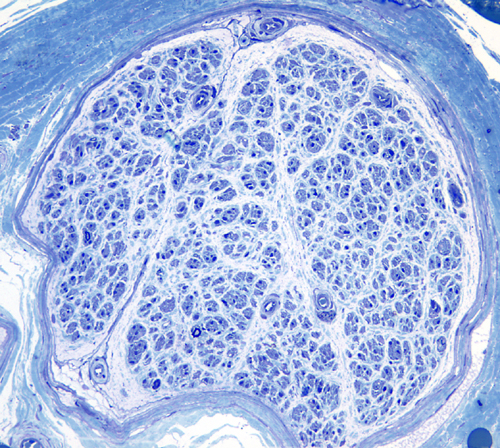
Peripheral nerves consist of fascicles that contain myelinated and unmyelinated axons. Endoneurium is the small amount of matrix that is present between individual axons. The perineurium is a sheath of special, fiber-like cells that ties the axons of each fascicle together. Epineurium is the connective tissue that surrounds the entire nerve trunk and gives off vascular connective tissue septa that traverse the nerve and separate fascicles from one another.
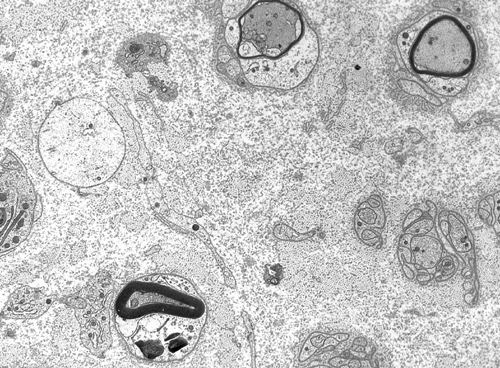
Axons thicker than one micron in the CNS and peripheral nervous system (PNS) are myelinated. Myelin is a spiral sheet of cell membrane wrapped around the axon. In the CNS, myelin is produced by oligodendroglial cells and in the PNS by Schwann cells. Each oligodendrocyte makes multiple segments of myelin that wrap around many axons. Each Schwann cell makes one segment of myelin. This is one reason why peripheral myelin regenerates more efficiently. Nodes of Ranvier are points of discontinuity between adjacent myelin sheaths in which the axon is not covered by myelin. Unmyelinated axons are covered by Schwann cell cytoplasm, but there is no spiraling of Schwann cell membrane around them.
The structure of central and peripheral myelin is essentially the same. Myelin is composed of 70% lipids and 30% protein. There are some important differences in myelin proteins between CNS and PNS. These differences explain why an allergic reaction against PNS myelin does not cause central demyelination and vice versa; and why inherited metabolic disorders of myelin proteins that affect peripheral nerves do not damage central myelin. On the other hand, lipids are similar between PNS and CNS myelin. For this reason, metabolic disorders of myelin lipids, such as metachromatic leukodystrophy, affect both, the central white matter and peripheral nerves.
The myelin sheath acts as an electrical insulator, preventing short-circuiting between axons. More important, it facilitates conduction. The nodes of Ranvier are the only points where the axon is uncovered by myelin and ions can be exchanged between it and the extracellular fluid. Depolarization of the axonal membrane at the nodes of Ranvier boosts the action potential that is transmitted along the axon and is the basis of saltatory (jumping) conduction.
PATHOLOGICAL PATTERNS OF NEUROPATHY
The pathology of peripheral neuropathy follows three basic patterns: Wallerian degeneration, distal axonopathy, and segmental demyelination.
Wallerian degeneration. The neuronal cell body maintains the axon through the axoplasmic flow. When an axon is transected, its distal part, including the myelin sheath, undergoes a series of changes leading to its complete structural disintegration and chemical degradation.
Changes also occur in the neuronal body. The RER disaggregates and the neuronal body balloons. The cytoplasm becomes smooth and the nucleus is displaced toward the periphery of the cell. This process is called central chromatolysis and reflects activation of protein synthesis in order to regenerate the axon. Cytoskeletal proteins and other materials flow down the axon. The proximal stump elongates at a rate of 1 to 3 mm per day. Schwann cells distal to the transection also proliferate and make new myelin.
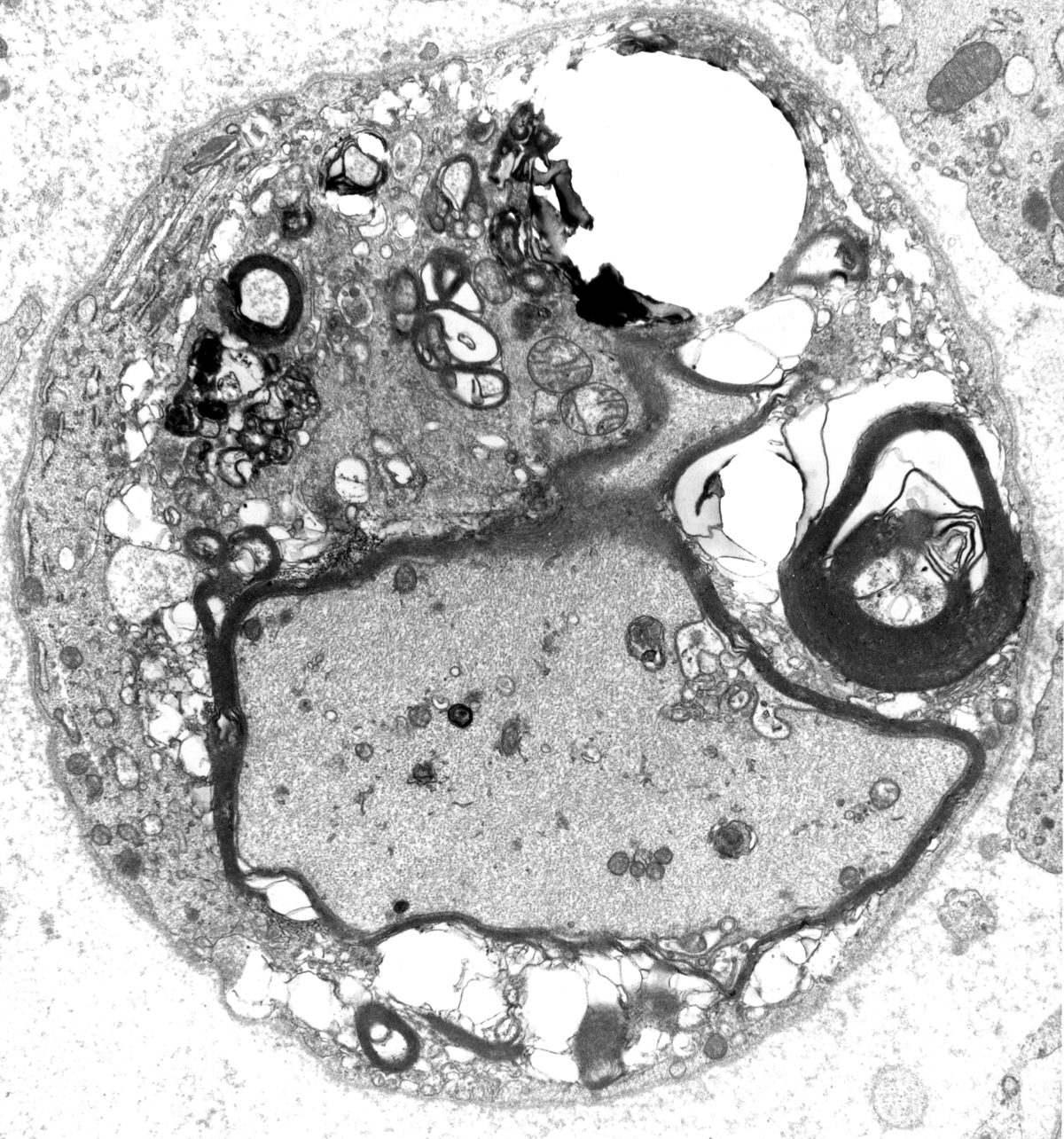
The degree of regeneration and recovery depends on how well the cut ends are put together and on the extent of soft tissue injury and scarring around the area of transection. If reconstruction is not good, a haphazard proliferation of collagen, Schwann cell processes, and axonal sprouts fill the gap, forming a traumatic neuroma. Wallerian degeneration was initially described in experimental axotomy. Neuropathies characterized by Wallerian degeneration include those that are caused by trauma, infarction of peripheral nerve (diabetic mononeuropathy, vasculitis) and neoplastic infiltration.
In distal axonopathy, degeneration of axon and myelin develops first in the most distal parts of the axon and, if the abnormality persists, the axon "dies back". This causes a characteristic distal ("stocking-glove") sensory loss and weakness. Neurofilaments and organelles accumulate in the degenerating axon (probably due to stagnation of axoplasmic flow). Eventually the axon becomes atrophic and breaks down. Severe distal axonopathy resembles Wallerian degeneration. At an advanced stage, there is loss of myelinated axons. Many clinically important neuropathies caused by drugs and industrial poisons such as pesticides, acrylamide, organic phosphates, and industrial solvents are characterized by distal axonopathy.
Distal axonopathy is thought to be caused by pathology of the neuronal body resulting in its inability to keep up with the metabolic demands of the axon. This explains why the disease begins in the most distal parts of nerves, and large axons that have the highest metabolic and nutritional demands are more severely affected. However, this question is not settled. It is hard to imagine how the relatively miniscule neuronal body can keep up with the metabolic demands of the enormous mass of the axon. Furthermore, the neuronal body is just as dependent on the distal axon and its synapses for trophic interactions that keep it alive and functioning.
Segmental demyelination, originally described in experimental lead poisoning, is characterized by breakdown and loss of myelin over a few segments. The axon remains intact and there is no change in the neuronal body. The loss of saltatory conduction that results from segmental demyelination leads to decrease of conduction velocity and conduction block. Deficits develop rapidly but are reversible because Schwann cells make new myelin. However, in many cases, demyelination leads to loss of axons and permanent deficits. The nerve, in segmental demyelination, shows demyelinated axons, thin-regenerating-myelin, "onion bulbs"(see below) and, in severe cases, loss of axons. The status of myelin can be evaluated with teased fiber preparations of peripheral nerves and by electron microscopy. Neuropathies characterized by segmental demyelination include acute and chronic inflammatory demyelinative neuropathies, diphtheritic neuropathy, metachromatic leukodystrophy and Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease.
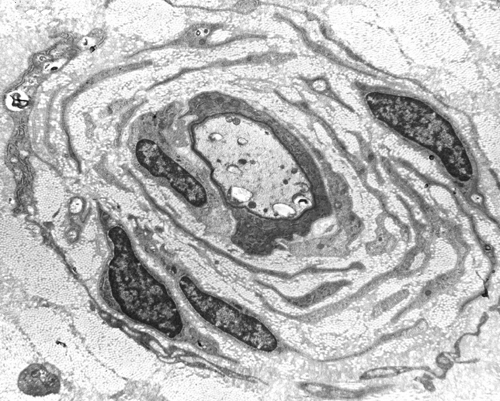
"Onion bulb" formations are concentric layers of Schwann cell processes and collagen around an axon. This proliferation is caused by repetitive segmental demyelination and regeneration of myelin and can cause gross thickening of peripheral nerves (hypertrophic neuropathy). The central axon is often demyelinated or has a thin layer of myelin. Onion bulb formations are the histological hallmark of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, but are also seen in other hereditary neuropathies (Dejerine-Sottas disease, Refsum disease), in diabetic neuropathy, and in chronic inflammatory demyelinative neuropathy.
The pathology of peripheral neuropathy is reflected in the spinal cord. Acute axonal neuropathy causes cental chromatolysis. Axonal neuropathy and distal axonopathy involving the bipolar neurons of the dorsal root ganglia cause degeneration of the central axons of these neurons in the gracile and cuneate tracts of the spinal cord. This lesion is associated with loss of position and vibration sense and sensory ataxia.
Neuropathies can be classified on the basis of their pathological changes into axonal (Wallerian degeneration and distal axonopathy), demyelinative, or mixed.
The pathological changes of most peripheral neuropathies (axonal degeneration, segmental demyelination or a combination of these) are not specific. In any active neuropathy, there are macrophages removing myelin and axon debris. Advanced axonal neuropathy shows loss of myelinated axons and increased endoneurial collagen. Some chronic demyelinative neuropathies show hypertrophic changes. Thus, in most neuropathies, the sural nerve biopsy can only establish the diagnosis of neuropathy and distinguish axonal from demyelinative and acute from chronic neuropathy, but cannot determine the cause of neuropathy. Only a few peripheral neuropathies show disease-specific pathological changes allowing a specific diagnosis. These neuropathies include acute and chronic inflammatory demyelinative neuropathies, hereditary motor and sensory neuropathies, vasculitis, sarcoid neuropathy, leprosy, amyloid neuropathy, neoplastic invasion of peripheral nerves, metachromatic leukodystrophy, adrenomyeloneuropathy, and giant axonal neuropathy.
APPROACH FOR THE INVESTIGATION OF PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY
The goal of the investigation of peripheral
neuropathy is to establish the diagnosis of peripheral neuropathy, determine
if it is an axonal or demyelinative process, and find its cause.
Clinically, neuropathy
causes weakness and atrophy of muscle,
loss of sensation or altered sensation (pain,
paresthesias), and weak or absent tendon reflexes. Nerve
conduction studies can distinguish
demyelinative neuropathy (slowing of conduction velocity
or conduction block) from axonal neuropathy (low-action
potential amplitudes). Electromyography
(EMG) can distinguish denervation atrophy from
primary muscle disease. CSF
examination is helpful, especially in inflammatory
demyelinative neuropathies. Because cranial and spinal
roots bathe in CSF, demyelinative neuropathies that
involve roots cause elevation of CSF protein. Also,
inflammation in nerve roots causes CSF pleocytosis.
Careful history taking with attention to family history,
environmental exposure, and systemic illness, combined
with neurological examination and laboratory studies
can determine the etiology in most peripheral neuropathies.
When the diagnosis is in doubt, a nerve biopsy studied
by light microscopy, electron microscopy, morphometry,
and teased fiber preparations can give more definitive
information. The sural nerve is usually chosen for
biopsy because it is superficial and easy to find
and it is predominantly sensory. Sural nerve biopsy
leaves a patch of hypesthesia in the lateral aspect
of the foot that is usually well tolerated.
Diabetic and other neuropathies
affect predominantly small myelinated and unmyelinated
fibers that convey pain and temperature sensation.
Degeneration in these "small fiber neuropathies" involves
the most distal portions of nerve fibers that are
found in different organs and tissues (somatic fibers)
rather than fibers in major nerves. Nerve conduction
studies and EMG in such cases may be normal and
the sural nerve biopsy may be difficult to interpret.
The diagnosis can be made with a skin biopsy.
A 3-4 mm plug of skin is removed with a punch and
sectioned with a microtome. The sections are treated
with antibodies to Protein Gene Product 9.5 which
reveal small nerve fibers that penetrate the epidermis.
The density of these fibers is reduced in small
fiber neuropathies.
PRINCIPAL CAUSES OF PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY
|
Further Reading
- Lauria G, Lombardi R. Skin biopsy: a new tool for diagnosing peripheral neuropathy. BMJ 2007;334:1159-62 PubMed
- Szigeti K, Lupski JR. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Eur J Hum Genet 2009;17:703-10. PubMed
- Gabreels-Festen A:Dejerine-Sottas syndrome grown to maturity: overview of genetic and morphological heterogeneity and follow up of 25 patients. J Anat 2002;200:341-56.PubMed
Updated: February, 2011