M2 NEUROPATHOLOGY LAB
QUIZ 5
Case A
Case B
Case C
Case D
Case E
Match the lettered case histories with the numbered images 21-25.
21 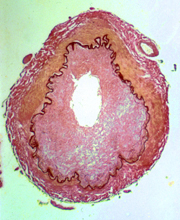 22
22 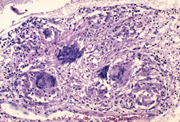 23
23 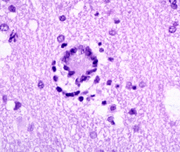 24
24 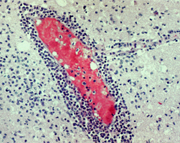 25
25 
Case A
An 89-year-old woman became progressively less active
two weeks prior to her admission and was found unresponsive
in bed on the day of admission. Her past medical
history was unremarkable. On admission, she had a
temperature of 39C, her neck was rigid and she had
left facial droop. Head CT was normal. CSF was slightly
cloudy with glucose 42 mg dl, protein 346 mg dl,
and 345 white blood cells (4% polys, 95% lymphocytes).
Gram stains and cytologic examination were negative.
Treatment with ampicillin was started. The patient
continued to be obtunded and chest x-rays, five days
after admission, showed an infiltrate in the right
lower lobe and pleural effusion. Bronchial aspirate
was positive for Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. Treatment
with antituberculosis medications was started. Over
the ensuing 10 days, left hemiparesis and seizures
developed, and the patient gradually lapsed into
a coma. She became progressively dyspneic and hypothermic
and died 23 days after admission.
Case B
An 18-year-old man who had just returned from the
Mardi Gras celebration in New Orleans developed a
sore throat, fever, headache, nausea and vomiting.
He became confused, and two days after the onset
of symptoms, his mother found him sitting up, drooling
and staring straight ahead. He did not respond to
her. En route to the hospital, he had a seizure.
A CSF was clear with 200 WBC’s (93% polys),
glucose 90 mg/dl and protein 91 mg/dl. Cultures were
negative. He became agitated and unresponsive. Seizures
continued. Brain MRI revealed hypodensity with enhancement
in frontal and temporal lobes. A repeat spinal tap
contained 350 cells, all lymphocytes. He was treated
with Acyclovir and Decadron, but deteriorated further
and died two weeks after admission.
Case C
A 35-year-old LPN was admitted to the hospital with
fever, confusion and severe headache. CSF was xanthochromic
with 1,051 WBC (98% neutrophils). Culture grew Neisseria
Meningitidis. She was treated with antibiotics. She
had seizures and confusion for one week. She was
discharged 27 days after admission. Six days after
discharge, she developed lethargy, seizures, and
left hemiparesis. She died of a massive right hemispheric
infarct.
Case D
A 31-year-old man with AIDS was admitted to the hospital
for neurological evaluation. He had been on AZT for
two years, but had been taking the medication erratically.
Two months before admission, he developed hand tremors.
Then he became progressively forgetful and weak.
Left leg weakness and foot drop appeared three weeks
before admission. His gait became ataxic, and his
speech was slow and slurred. He was disoriented.
There was no evidence of systemic infection. Brain
MRI revealed mild bilateral diffuse white matter
hypodensity. CSF showed 4 lymphocytes and normal
protein and glucose. A brain biopsy was done.
Case E
A 26-year-old woman had weakness of the right leg,
then of the left leg, and numbness of the hands and
perioral area. She recovered without treatment but,
three years later, she suddenly developed paraplegia,
blindness and aphasia. She made a good recovery and
was able to function for the next 9 years, except
for slight residual weakness. Then, paraplegia recurred
with spasms of the legs. She also suffered left facial
paralysis and nystagmus. CSF showed 25 WBC’s,
all lymphs, and normal protein and glucose. Tendon
reflexes were brisk, and plantar responses were extensor.
Subsequently she became incontinent. From that point
on, her condition remained unchanged. She became
demented, had frequent urinary tract infections and
died of pneumonia at age 47.
ALL LECTURE PODCASTS ARE EMBEDDED IN THEIR RESPECTIVE
NEUROPATHOLOGY PAGES AND CAN ALSO BE FOUND ON THE
VIMEO CHANNEL "DIMITRI
AGAMANOLIS NEUROPATHOLOGY"